Small Language Model RAGs is All You Need
A comprehensive analysis of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems based on different language models, with a particular focus on the performance of small language models compared to their larger counterparts.
Introduction
In the current AI landscape, the quest for efficient and effective language models has led researchers and practitioners to explore various approaches. One such promising technique is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which combines the power of language models with external knowledge retrieval. We are going to do a comprehensive analysis of RAG systems based on different language models, with a particular focus on the performance of smaller models compared to their larger counterparts.
As AI continues to permeate various industries and applications, there’s a growing need for systems that can deliver high-quality, faithful, and relevant responses while efficiently utilizing context. Traditional wisdom might suggest that larger language models would invariably outperform smaller ones. However, with our experiments, we are going to show surprising and promising results that challenge this assumption.
We will explore the following topics in our analysis:
- The competitive performance of smaller language models in RAG systems
- The effectiveness of innovative techniques like Mixture RAG pipelines inspired by the Mixture of Agents (MoA) technique
- The importance of model architecture and training strategies over sheer size
- The particular strengths of smaller models in context utilization
- The additional benefits of using smaller language models, including self-hosting capabilities, improved efficiency, and democratization of AI
By examining these aspects, we aim to shed light on the potential of smaller language models and sophisticated RAG approaches to deliver powerful AI capabilities while offering greater flexibility, control, and cost-effectiveness.
Setup
In this section, we will provide an overview of the dataset used for the experiments and the RAG pipeline setup. In total there were 28 experiments conducted in total.
Dataset
The dataset used for the experiments is a collection of research papers in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP), specifically focusing on Large Language Models (LLMs). The dataset consists of the 15 most cited papers in the field of NLP and LLMs. The papers included in the dataset are:
- BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding
- The Claude 3 Model Family: Opus, Sonnet, Haiku
- Gemma: Open Models Based on Gemini Research and Technology
- Gemma 2: Improving Open Language Models at a Practical Size
- Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training
- Language Models are Few-Shot Learners
- GPT-4 Technical Report
- GPT-4o System Card
- LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models
- Llama 2: Open Foundation and Fine-Tuned Chat Models
- The Llama 3 Herd of Models
- Mistral 7B
- Mixtral of Experts
- Mixture-of-Agents Enhances Large Language Model Capabilities
- Attention Is All You Need
Questions from these papers were used as the evaluation dataset for the experiments. The questions included in the evaluation dataset are:
- “What are the two tasks in BERT?”
- “Does Claude 3 models have vision capabilities?”
- “On what architecture the Gemma model is based on?”
- “What tokenizer is used in the Gemma2 model?”
- “How many stages of training are in the GPT model?”
- “On what architecture the GPT-3 model is based on?”
- “Can the GPT-4 model accept both text and image inputs?”
- “What is GPT-4o model?”
- “What optimizer is used for LLaMA?”
- “What is the difference between the Llama 2 and Llama 2-Chat?”
- “How many stages are there in the development of the Llama 3 model?”
- “What is sliding window attention?”
- “Is Mixtral based on the idea of a mixture of experts?”
- “What is Mixture of Agents?”
- “How can attention be described in the Transformer?”
The creation of the evaluation dataset (questions) was done by extracting the questions which capture the essence of the papers. The questions were selected based on their relevance to the content of the papers and their potential to evaluate the performance of the RAG systems. The questions were designed to test the faithfulness, answer relevancy, and context utilization of the RAG systems, providing a comprehensive evaluation of their capabilities.
RAG Pipeline Setup
All the experimental pipelines share these common components:
- Chunker: The dataset is chunked into smaller parts to be used for the experiments. The chunk size is 1500 and the chunk overlap is 100.
- Embedder: The Amazon Titan Embed Text model is used to embed the chunks of the dataset, with 512 vector dimensions which are normalized.
- Vector Store: The embedded vectors are stored in a FAISS vector database for faster retrieval.
- Retriever: The retrieval of the most similar chunks is done using the FAISS vector database. The number of similar chunks retrieved is 5 and the search type is similarity.
The experimental pipelines differ in the LLMs used and the way of the LLMs are used/combined.
The LLM used in the pipelines are:
- gemma2-9b-it - Small LLM
- gemma-7b-it - Small LLM
- mistral-7b-instruct - Small LLM
- mixtral-8x7b-instruct - Small LLM
- llama-3-8b-instruct - Small LLM
- llama-3.1-8b-instruct - Small LLM
- llama-3-70b-instruct - Large LLM
- llama-3.1-70b-instruct - Large LLM
- llama-3.1-405b-instruct - Large LLM
- claude-3-haiku - Small LLM
- claude-3-sonnet - Large LLM
- claude-3-opus - Large LLM
- claude-3-5-sonnet - Large LLM
- gpt-4o - Large LLM
- gpt-4o-mini - Large LLM
- gpt-4-turbo - Large LLM
The LLMs used in the experiments are from different providers like AWS Bedrock, Groq, and OpenAI. All the experiments were done on 27th and 28th of September 2024, so the results may vary if the experiments are run on different dates, because the versions of the models may change if they are trained again on newer data.
Each of the LLMs have specific instruction prompt templates that are used for the experiments. Those templates can be found on:
All of the LLMs that are used in the RAG pipelines have the same parameters:
- temperature: 0
- In short, the lower the temperature, the more deterministic the results in the sense that the highest probable next token is always picked. Increasing temperature could lead to more randomness, which encourages more diverse or creative outputs. You are essentially increasing the weights of the other possible tokens. In terms of application, you might want to use a lower temperature value for tasks like fact-based QA to encourage more factual and concise responses. For poem generation or other creative tasks, it might be beneficial to increase the temperature value.
- max_tokens: 4096
- This parameter sets the maximum number of tokens that the model can generate in a single response. It ensures that the output does not exceed a certain length, which is useful for controlling the verbosity of the responses.
- top_p: 0
- A sampling technique with temperature, called nucleus sampling, where you can control how deterministic the model is. If you are looking for exact and factual answers keep this low. If you are looking for more diverse responses, increase to a higher value. If you use Top P it means that only the tokens comprising the top_p probability mass are considered for responses, so a low top_p value selects the most confident responses. This means that a high top_p value will enable the model to look at more possible words, including less likely ones, leading to more diverse outputs.
We utilized two different RAG pipeline configurations for the experiments:
- Simple RAG Pipeline: Uses a single LLM to generate the responses.
- Mixture RAG Pipeline: Uses multiple LLMs to generate the responses, which are then aggregated by another LLM.
Let’s dive into the details of each pipeline configuration.
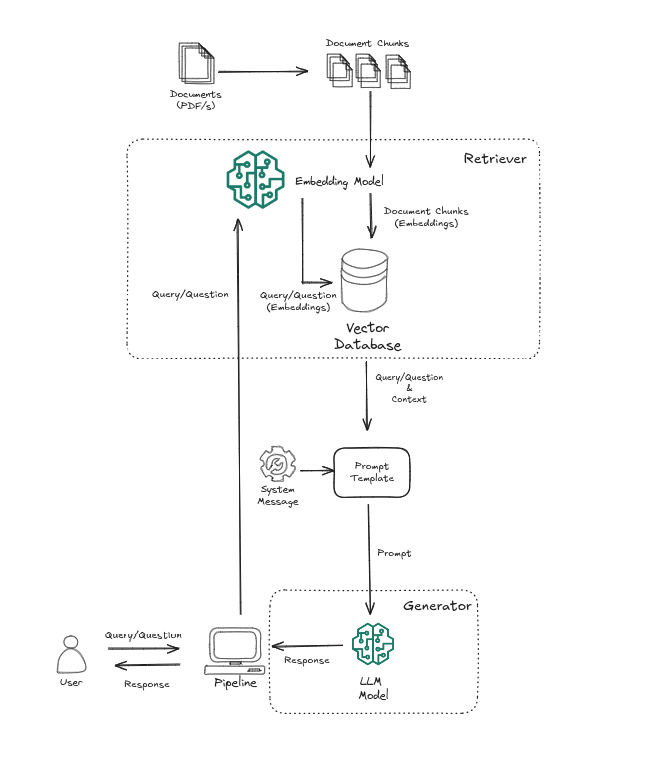
Simple RAG Pipeline
The Simple RAG pipeline uses a single LLM to generate the responses. This is how the Simple RAG looks:
For all the experiments the system and the user messages are the same:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
system_message:
"You are an assistant that has a lot of knowledge about Large Language Models.
Answer the user's question in a way that is easy to understand and informative.
Use the provided context to generate a response that is relevant and accurate.
You are an assistant that has a lot of knowledge about Large Language Models.
Answer the user's question in a way that is easy to understand and informative.
Use the provided context to generate a response that is relevant and accurate."
user_message: "Please answer my question based on the provided context:"
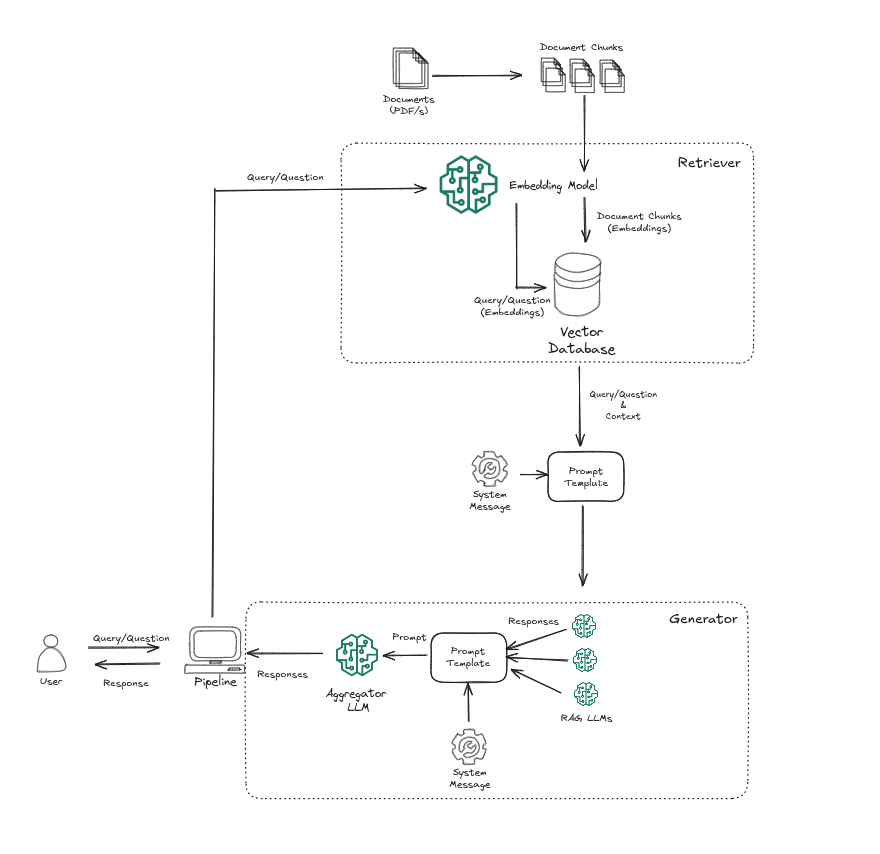
Mixture RAG Pipeline
The Mixture RAG pipeline is mostly is like the Simple RAG pipeline, but in the Generator we basically trigger multiple LLMs (Simple RAGs with the same prompt system and user messages previously defined) to generate the responses, and those responses are the aggregated by another LLM. This is how the Mixture RAG looks:
There are three different system and user message combinations used for the experiments, for the aggregation LLM:
- One combination is really similar to the one used in the Mixture of Agents (MoA) implementation:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
system_message:
You have been provided with a set of responses from various small language models to the latest user query.
Your task is to synthesize these responses into a single, high-quality response.
It is crucial to critically evaluate the information provided in these responses, recognizing that some of it may be biased or incorrect.
Your response should not simply replicate the given answers but should offer a refined, accurate, and comprehensive reply.
Ensure your response is well-structured, coherent, and adheres to the highest standards of accuracy and reliability.
user_message: "Please synthesize the responses from the small language models and give me only the most accurate information."
- The second combination is a bit modified from the first one:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
system_message:
You have been provided with a set of responses from various small language models to the latest user query.
The responses of the small language models are based on the context provided in the user query.
Your task is to create a single, high-quality response based on the responses of the small language models.
You should perform something like a ensemble model based on majority voting.
Your response should be very accurate and informative, while keeping the faithfulness and relevance to the previous responses.
user_message: "Please generate a single response based on the provided responses:"
- The third combination is basically making the aggregator LLM to choose the best response from the generated responses (thought):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
system_message:
You have been provided with a set of responses from various small language models to the latest user query.
The responses of the small language models are based on the context provided in the user query.
Your task is to choose the best response from the provided responses.
You should choose the response by analyzing all available responses and selecting the one you think is the most accurate and informative.
Keep in mind the response must be a high-quality response, while getting the most faithful and relevant information from the provided responses.
When you have made your choice, make that your final response and do not provide any additional responses, like explanations or clarifications why you chose that response.
user_message: "Please choose a single response based on the provided responses:"
Methodology
All of the results are based on the evaluation of the experiments using the evaluation dataset. In this section, we will present the results of the experiments and analyze the performance of the RAG systems based on different language models. The evaluation metrics used for the analysis are faithfulness, answer relevancy, and context utilization. For calculating the metrics, the judge evaluator LLM and Embedder are used to generate the ground truth answers and to calculate the scores.
The evaluation was done using Ragas. Ragas is a framework that helps to evaluate Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines. There are existing tools and frameworks that help you build these pipelines but evaluating it and quantifying your pipeline performance can be hard. This is where Ragas (RAG Assessment) comes in.
Metrics
The metrics used for the evaluation of the experiments are:
- Faithfulness: This measures the factual consistency of the generated answer against the given context. It is calculated from answer and retrieved context. The answer is scaled to (0,1) range. Higher the better. The generated answer is regarded as faithful if all the claims made in the answer can be inferred from the given context. To calculate this, a set of claims from the generated answer is first identified. Then each of these claims is cross-checked with the given context to determine if it can be inferred from the context.
- Answer Relevancy: The evaluation metric, Answer Relevancy, focuses on assessing how pertinent the generated answer is to the given prompt. A lower score is assigned to answers that are incomplete or contain redundant information, and higher scores indicate better relevancy. This metric is computed using the question, the context and the answer. The Answer Relevancy is defined as the mean cosine similarity of the original question to a number of artificial questions that were generated (reverse engineered) based on the answer:
Where:
- is the embedding of the
artificial question generated from the answer.
- is the embedding of the original question.
- is the number of artificial questions generated from the answer.
Even though in practice the score will range between 0 and 1 most of the time, this is not mathematically guaranteed, due to the nature of the cosine similarity, which ranges from -1 to 1.
- Context Utilization: Context utilization measures the extent to which the retrieved context aligns with the annotated answer, treated as the ground truth. It is computed using question, ground truth and the retrieved context, and the values range between 0 and 1, with higher values indicating better performance. To estimate context utilization from the ground truth answer, each claim in the ground truth answer is analyzed to determine whether it can be attributed to the retrieved context or not. In an ideal scenario, all claims in the ground truth answer should be attributable to the retrieved context. If the ground truth is not provided, the judge evaluator LLM is used to generate the ground truth answer.
Judge LLM and Embedder
For the Judge LLM Evaluator, we utilized the Claude 3.5 Sonnet model with the model ID anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620-v1:0. This model was configured with a maximum token limit of 4096 and a temperature setting of 0 to control the randomness of the output. Additionally, we employed the Amazon Titan Embed Text 2 model with the model ID amazon.titan-embed-text-v2:0, which operates with 512 dimensions and normalization enabled.
Results and Analysis
The initial exploration of the results focused on identifying problematic questions, specifically those with lower scores. The objective was to refine the experiments by excluding these less effective questions and concentrating on the 10 most relevant ones. This approach aims to enhance the overall quality and reliability of the experiments by ensuring that only the most pertinent questions and answers are considered.
To identify these problematic questions, the dataset was grouped by individual questions. For each question, the mean scores were calculated across three key metrics: faithfulness, answer relevancy, and context utilization. These mean scores provided a comprehensive view of each question’s performance. Subsequently, an overall average score was computed for each question by taking the basic average of the mean scores from the three metrics. This overall score was then used to rank the questions, allowing for an informed decision on which questions to exclude from the experiments.
Monitoring the RAGs and Traces (Tracebility & Observability)
The experiments were monitored using the Langfuse, which provides detailed traces and metrics for each experiment. Langfuse is an open-source LLM engineering platform that helps teams collaboratively debug, analyze, and iterate on their LLM applications.
The traces include information about the execution of the RAG pipelines, the interactions with the LLMs, and the performance of the experiments. The traces are stored in the Langfuse Server and can be accessed through the Langfuse API. The traces provide valuable insights into the behavior of the RAG systems and help in identifying potential issues or areas for improvement. Additionally, the traces can be used to analyze the performance of the RAG systems and evaluate the quality of the generated responses. To each of the trace we attach the scores for the faithfulness, answer relevancy, and context utilization metrics, calculated using the Judge LLM and Embedder.
Questions with the lowest scores
| Index | Question | Score |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | How many stages are there in the development of the Llama 3 model? | 0.932122 |
| 2 | Does Claude 3 models have vision capabilities? | 0.929947 |
| 3 | What is the GPT-4o model? | 0.881287 |
| 4 | On what architecture the Gemma model is based on? | 0.856614 |
| 5 | How many stages of training are in the GPT model? | 0.851652 |
| 6 | What is the difference between the Llama 2 and Llama 2-Chat? | 0.840406 |
| 7 | Is Mixtral based on the idea of a mixture of experts? | 0.838570 |
| 8 | Can the GPT-4 model accept both text and image inputs? | 0.823327 |
| 9 | What tokenizer is used in the Gemma2 model? | 0.782223 |
| 10 | What is Mixture of Agents? | 0.767041 |
| 11 | What are the two tasks in BERT? | 0.763584 |
| 12 | What is sliding window attention? | 0.748468 |
| 13 | How can attention be described in the Transformer? | 0.728414 |
| 14 | What is optimizer is used for LLaMA? | 0.614411 |
| 15 | On what architecture the GPT-3 model is based on? | 0.570796 |
From the table, we can observe which questions have the lowest scores. Specifically, the last five questions exhibit the lowest performance and are therefore excluded from the subsequent analysis. This exclusion helps to focus the analysis on the more reliable and relevant questions, ensuring that the results are not skewed by outliers or less effective queries.
The next step involves a detailed analysis of the results for each experiment. This analysis includes ranking the experiments based on the average scores for each metric: faithfulness, answer relevancy, and context utilization. For clarity and comprehensiveness, the top 14 experiments for each metric are highlighted and presented below. Additionally, an overall ranking is conducted by calculating the average of the average scores across all metrics. This comprehensive ranking provides a holistic view of the experiments’ performance, facilitating a more informed evaluation and comparison.
Faithfulness
| Index | Experiment | Faithfulness |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | simple-rag-gpt-4o | 0.950794 |
| 2 | simple-rag-llama-3.1-405b-instruct | 0.935850 |
| 3 | simple-rag-llama-3.1-8b-instruct | 0.913799 |
| 4 | simple-rag-llama-3.1-70b-instructed | 0.913709 |
| 5 | simple-rag-mistral-7b-instruct | 0.905000 |
| 6 | simple-rag-gemma-7b-it | 0.902381 |
| 7 | simple-rag-gpt-4o-mini | 0.872143 |
| 8 | simple-rag-llama-3-70b-instruct | 0.869946 |
| 9 | mixture-rag-mixtral-8x7-instruct-modified | 0.868546 |
| 10 | mixture-rag-llama3.1-8b-instruct-thought | 0.866354 |
| 11 | simple-rag-llama-3-8b-instruct | 0.862557 |
| 12 | simple-rag-mixtral-8x7b-instruct | 0.862047 |
| 13 | simple-rag-claude-3-opus | 0.861019 |
| 14 | simple-rag-gpt-4-turbo | 0.860575 |
| 15 | simple-rag-claude-3-sonnet | 0.950794 |
The table above ranks various experiments based on their faithfulness scores, which measure how accurately the generated responses adhere to the source information. Based on the results from the table, it is evident that the scores of the RAG systems based on smaller language models are very close to, or in some cases even better than, those based on larger language models. For instance, in the top 10 scores, we have 5 RAG systems that are based on smaller language models: simple-rag-llama-3.1-8b-instruct, simple-rag-mistral-7b-instruct, simple-rag-gemma-7b-it, mixture-rag-mixtral-8x7-instruct-modified- which is a combination of multiple smaller language models and mixture-rag-llama3.1-8b-instruct-thought- also a combination of multiple smaller language models with specific prompt. These smaller models achieve faithfulness scores of 0.913799, 0.905000, 0.902381, 0.868546 and 0.866354 respectively, which are comparable to or even surpass the scores of some larger models.
This observation suggests that smaller language models can perform nearly as well as, or sometimes better than, larger models in terms of faithfulness. The close scores among the top experiments indicate that model architecture and training strategies play a significant role in achieving high faithfulness, regardless of the model size. This insight is valuable for guiding future improvements and optimizations in model development, as it highlights the potential of smaller models to deliver high-quality results, results that are faithful to the context and source information provided.
Answer Relevancy
| Index | Experiment | Answer Relevancy |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | simple-rag-mistral-7b-instruct | 0.903208 |
| 2 | simple-rag-gpt-4o-mini | 0.902027 |
| 3 | simple-rag-gemma2-9b-it | 0.898397 |
| 4 | simple-rag-llama-3.1-8b-instruct | 0.889998 |
| 5 | simple-rag-claude-3.5-sonnet | 0.887503 |
| 6 | mixture-rag-gemma2-9b-it-thought | 0.880448 |
| 7 | mixture-rag-gemma2-9b-it-modified | 0.875354 |
| 8 | simple-rag-mixtral-8x7b-instruct | 0.871510 |
| 9 | simple-rag-claude-3-opus | 0.869271 |
| 10 | simple-rag-claude-3-sonnet | 0.868577 |
| 11 | mixture-rag-mixtral-8x7-instruct-thought | 0.868344 |
| 12 | simple-rag-gpt-4o | 0.868135 |
| 13 | simple-rag-gpt-4-turbo | 0.866888 |
| 14 | simple-rag-claude-3-haiku | 0.863664 |
| 15 | simple-rag-gemma-7b-it | 0.863156 |
The table above ranks various experiments based on their answer relevancy scores, which measure the relevance of the generated responses to the given prompts. The results show that in the top 10 experiments, 6 of them are again based on smaller language models with simple rag pipeline approach or with the smart technique of mixture rag pipeline approach. The experiments simple-rag-mistral-7b-instruct, simple-rag-gemma2-9b-it, simple-rag-llama-3.1-8b-instruct, mixture-rag-gemma2-9b-it-thought, mixture-rag-gemma2-9b-it-modified and simple-rag-mixtral-8x7b-instruct have really high answer relevancy scores of 0.903208, 0.898397, 0.889998, 0.880448, 0.875354 and 0.871510 respectively.
This again indicates that smaller language models can generate highly relevant responses that are closely aligned with the given prompts. We can even see that the Mixture RAG pipeline approach with the smart technique of choosing the best response from the generated responses(thought) can achieve high answer relevancy scores.
Context Utilization
| Index | Experiment | Context Utilization |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | mixture-rag-claude-3-haiku-thought | 0.933333 |
| 2 | simple-rag-mistral-7b-instruct | 0.925000 |
| 3 | mixture-rag-claude-3-haiku | 0.916667 |
| 4 | mixture-rag-gemma2-9b-it-modified | 0.916667 |
| 5 | mixture-rag-llama3.1-8b-instruct-modified | 0.908333 |
| 6 | simple-rag-gpt-4o | 0.905556 |
| 7 | mixture-rag-mixtral-8x7-instruct-thought | 0.900000 |
| 8 | mixture-rag-llama3.1-8b-instruct-thought | 0.897222 |
| 9 | simple-rag-llama-3-70b-instruct | 0.897222 |
| 10 | mixture-rag-gemma2-9b-it-thought | 0.897222 |
| 11 | simple-rag-gemma-7b-it | 0.897222 |
| 12 | simple-rag-llama-3.1-70b-instructed | 0.897222 |
| 13 | simple-rag-claude-3-haiku | 0.894444 |
| 14 | simple-rag-gpt-4o-mini | 0.888889 |
| 15 | simple-rag-gpt-4-turbo | 0.888889 |
The table above ranks various experiments based on their context utilization scores, which measure how effectively the retrieved context aligns with the annotated answers. Here really we can see how RAG systems based on smaller language models are performing really well in terms of context utilization. From the best 10 experiments, 6 of them are based on smaller language models. Another interesting thing is that Mixture RAG approaches are excellent in context utilization, with 2 of the top 5 experiments being based on the Mixture RAG approach. The experiments mixture-rag-llama3.1-8b-instruct, mixture-rag-mixtral-8x7-instruct-modified, and mixture-rag-mixtral-8x7-instruct have context utilization scores of 0.916667, 0.916667, and 0.913889 respectively.
Average of the Scores
| Index | Experiment | Average Score |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | simple-rag-mistral-7b-instruct | 0.911069 |
| 2 | simple-rag-gpt-4o | 0.908161 |
| 3 | simple-rag-llama-3.1-8b-instruct | 0.890155 |
| 4 | simple-rag-gpt-4o-mini | 0.887686 |
| 5 | simple-rag-gemma-7b-it | 0.887586 |
| 6 | simple-rag-llama-3.1-70b-instruct | 0.880033 |
| 7 | simple-rag-llama-3-70b-instruct | 0.876048 |
| 8 | simple-rag-gemma2-9b-it | 0.874335 |
| 9 | simple-rag-mixtral-8x7b-instruct | 0.872297 |
| 10 | simple-rag-gpt-4-turbo | 0.872117 |
| 11 | simple-rag-llama-3.1-405b-instruct | 0.871293 |
| 12 | mixture-rag-gemma2-9b-it-modified | 0.869955 |
| 13 | mixture-rag-llama3.1-8b-instruct-thought | 0.869177 |
| 14 | simple-rag-claude-3-haiku- | 0.860552 |
| 15 | mixture-rag-gemma2-9b-it-thought | 0.860197 |
The table above ranks various experiments based on their average scores, which provide a comprehensive view of the experiments’ performance across all metrics. The results show the dominance of RAG systems based on smaller language models, with 9 of the top 15 experiments being based on smaller models.
Conclusion
The analysis of various experiments comparing RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) systems based on different language models yields several significant insights:
Smaller language models perform competitively when used in RAG system, often achieving scores comparable to or even surpassing those of larger language models based RAG systems across multiple metrics (faithfulness, answer relevancy, and context utilization).
The mixture RAG pipeline where the generator of the RAG system is inspired by the implementation of Mixture of Agents(MoA) technique like choosing the best response from generated output options, shows strong performance across metrics.
The close scores among top experiments suggest that factors such as model architecture and training strategies may be more crucial than model size in achieving high-quality results.
Smaller models and mixture RAG approaches demonstrate particular effectiveness in context utilization, indicating their ability to align retrieved information with annotated answers.
Overall when considering average scores across all metrics, RAG systems based on smaller language models dominate the top rankings, occupying 9 out of the top 14 positions.
These findings highlight the potential of smaller language models and sophisticated RAG approaches to deliver high-quality, faithful, and relevant responses while efficiently utilizing context.
Moreover, we do not need to work the additional benefits of the smaller language models, such as:
Self-hosting and open-source capabilities: Smaller models are more amenable to self-hosting, allowing organizations to maintain control over their data and infrastructure. Many of these models are also open-source, fostering transparency, community-driven improvements, and customization.
Improved efficiency and reduced costs: Smaller models require less computational resources, leading to lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs. This efficiency makes them more environmentally friendly and economically viable for a broader range of applications.
Democratization of AI: The ability to run these models on less powerful hardware democratizes access to advanced AI capabilities. This allows individuals, small businesses, and organizations with limited resources to create and deploy sophisticated RAG systems, fostering innovation across diverse sectors.
Faster inference times: Smaller models typically offer quicker response times, which is crucial for real-time applications and enhancing user experience in interactive systems.
Privacy and compliance advantages: Self-hosted smaller models can help organizations better comply with data protection regulations and maintain stricter control over sensitive information.
Flexibility and adaptability: Smaller models are often easier to fine-tune or adapt to specific domains or tasks, allowing for more tailored solutions without the need for extensive computational resources.
Ability to run on edge devices: Smaller models can be deployed on edge devices, enabling AI applications to operate locally without relying on cloud services. This capability is essential for scenarios where low latency, privacy, or limited network connectivity are critical.
These insights and benefits could guide future developments in language model applications, potentially leading to more resource-efficient, accessible, and equally effective AI systems. By leveraging smaller language models in RAG systems, organizations and individuals can harness powerful AI capabilities while enjoying greater flexibility, control, and cost-effectiveness.